Scientists are looking for alternative energy sources as fossil fuels are becoming more expensive and scarce. Hydrogen has long been regarded as an ideal source because it does not pollute when burnt. The issue has been determining cost-effective methods of producing hydrogen.
Water is the most abundant form of hydrogen on Earth. It exists as a gas in the atmosphere in trace amounts – less than one part per million by volume. Any hydrogen that does enter the atmosphere quickly escapes the gravity of the Earth and enters outer space. There are several methods for producing hydrogen, one of which is Photo electrolysis, which generates electricity by splitting water molecules using photovoltaic cells, is one new approach being investigated.
What is Electrolysis?
Electrolysis is the process by which ionic substances are decomposed into simpler substances when an electric current is passed through them.
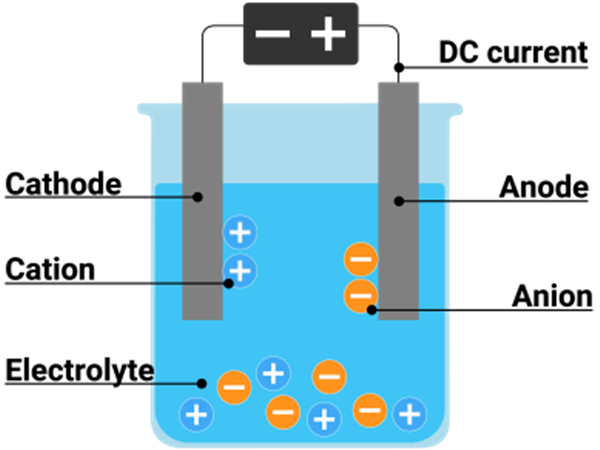
Electrolysis requires three main components: an electrolyte, electrodes, and an external power source.
An electrolyte is a chemical substance that contains free ions and conducts electricity (e.g. an ion-conducting polymer, solution, or an ionic liquid compound). Electrolysis cannot occur if the ions are not mobile, as in most solid salts.
The electrodes are immersed and spaced apart so that a current flows between them through the electrolyte and are connected to the power source, completing the electrical circuit. The reaction is driven by a direct current supplied by the power source, which attracts ions in the electrolyte to the respective oppositely charged electrode.
Production of Hydrogen by Water Electrolysis
Water electrolysis is the process of converting water (H2O) into hydrogen (H+) and hydroxide (OH–) ions by passing an electric current through it. Ions move to opposite electrodes, releasing pure hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) gases. It is an oxidation-reduction reaction that does not occur spontaneously. Because the heat in the form of electricity is supplied to the electrolytic cell, the reaction is endothermic. The chemical reaction for water electrolysis can be divided into two halves that take place at the cathode and anode.
At the cathode, hydrogen ions acquire electrons and are converted into hydrogen gas in a reduction reaction. The following is a half-reaction:
2H+ (aq.) + 2 e– → H2 (g)
An oxidation reaction occurs when water molecules transfer electrons to the anode and release oxygen gas. The half-reaction is depicted below.
2H2O (l) → O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq.) + 4 e–
Overall, the chemical reaction is
2H2O (l) → 2H2 (g) + O2 (g)
The water electrolysis reaction thus demonstrates the separation of hydrogen and oxygen from water. Two moles of water yield two moles of hydrogen and one mole of oxygen. The amount of hydrogen produced is twice that of oxygen. Charges are also exchanged between the electrodes and the electrolyte. Two electrons are transferred from the cathode to the electrolyte for every mole of hydrogen. Four electrons are transferred from the electrolyte to the anode for every mole of oxygen.
Water electrolysis can also be performed in an alkali medium. The following are the half-reactions in this case:
Cathode (reduction): 2H2O (l) + 2e– → H2 (g) + 2OH– (aq)
Anode (oxidation): 4OH– (aq.) → O2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + 4e–
The water electrolysis equation is obtained by combining the two half-reactions.
2H2O (l) → 2H2 (g) + O2 (g)
Summary
- Electrolysis is a promising method for producing carbon-free hydrogen from renewable and nuclear resources.
- The process of splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity is known as electrolysis.
- In an alkali medium, water electrolysis can also be performed.